|
VII.
Histoplasmosis
|
|
Case 47:
Histoplasmosis / Carcinoma
|
|
|
|
Histoplasmosis
|
|
Carcinoma
|
|
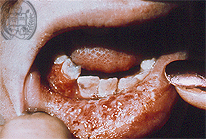
Fig.47-A1
Histoplasmosis
This patient presents a diffuse swelling of the lower lip with an extensive tumor-like ulceration. This is a secondary infection after haematogenous dissemination. The primary infection took place after the inhalation of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum, the classical small variety of the genus Histoplasma capsulatum a so called dimorphic fungus with formation of foci in the lungs, often as a primary complex.
|
|
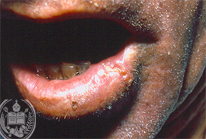
Fig.47-B1
Carcinoma
The nodular alterations on the lower lip of this patient have a partly different size and are ulcerated.
|
|
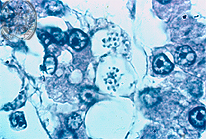
Fig.47-A2
Histoplasmosis
The small granular-like fungus cells of H. caps. var. capsulatum are yeast-like in the tissues and have a size of 2-4 µ. Here they are seen with high power in the HE stain and are intracellularly arranged. The other variety of the genus Histoplasma capsulatum is called H.caps.var duboisii which are large yeast cells reaching the size of 15-20 µ. The autochthonous infection of this mycosis occurs only in Central Africa and apparently also by inhalation. The skin and Fig bones are mostly affected. The histological aspect of this variety will be shown in case 50.
|
|

Fig.47-B2
Carcinoma
Histologically a squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed.
|
|
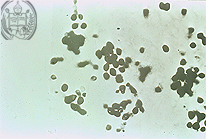
Fig.47-A3
Histoplasmosis
The small yeast-like fungus cells of H. capsulatum var. capsulatum stain black with the Grocott method as all the other fungus cells. These fungi are often arranged in small (intracellular) clusters.
|
|
|
|
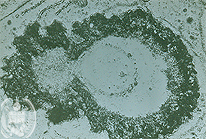
Fig.47-A4
Histoplasmosis
The small yeast-like fungus cells multiply in tissues by singular budding. The daughter cells mostly are smaller than the mother cell. This picture is made by electron microscopy.
|
|
|
|

Fig.47-A5
Histoplasmosis
The tissue reactions in this fungal infection are different depending on the acute or chronic evolution of the infection. In the last a granulomatous reaction with giant cells is present and mostly only a few fungus cells are recognized in the tissue. At this low power fungus cells can not be detected. HE stain.
|
|
|
| español | english | deutsch |
|
|