|
XII.
Actinomycosis
|
|
Case 62:
Actinomycosis / Alveolar fistula
|
|
|
|
Actinomycosis
|
|
Alveolar fistula
|
|
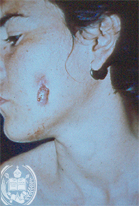
Fig.62-A1
Actinomycosis
In this young girl from the State Barinas developed an ulcer in the mandibular region with a diameter of 2 cm and the presence of a small hole of a fistula in the centre. This fistula discharged occasionally small yellowish granules.
|
|
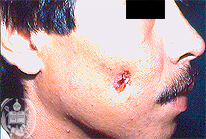
Fig.62-B1
Alveolar fistula
The cheek of this patient shows a skin lesion very similar to an actinomycotic infection with a central fistula. The process developed after a periodontitis with radiculitis.
|
|
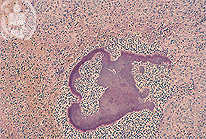
Fig.62-A2
Actinomycosis
The biopsy slide stained with the HE method shows in the abscesses the presence of irregular formed blackish -blue clusters. These are typical grains of the bacteria Actinomyces israeli. The actinomycetes earlier were classified as fungi. Today they are reclassified and belong to the bacteria, but kept their fungal name. In German they were called "ray fungi" and the disease got a similar name. In animals the Actinomyces bovis is the species causing actinomycosis. In the industrial countries this infection nowadays is seldom, but it is seen still relatively frequent in the developing countries and in the tropics.
|
|
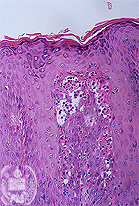
Fig.62-B2
Alveolar fistula
Histologically a non-specific inflammation is seen with haemosiderin pigment. HE stain.
|
|

Fig.62-A3
Actinomycosis
The grain of fig. 62-A2 is stained black here with the special fungus stain, the Grocott method. On the surface of the grain the filamentous structure of the actinomycetes may be recognized. The localization of the infection is typical in this.
|
|

Fig.62-B3
Alveolar fistula
In the superficial layers of the skin blackish fungal hyphae are observed representing a secondary dermatophytosis caused by Tinea versicolour. Grocott method.
|
| español | english | deutsch |
|
|